FCC Primer for CORI’s MDA
We rely on two key datasets from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
- National Broadband Map (NBM):
- Provides granular information on broadband service availability at specific locations, including details about service providers, technology types, and advertised speeds.
- Broadband Funding Map (BFM):
- Offers insights into federally funded broadband infrastructure projects, detailing program boundaries and project-level information.
Both datasets are publicly available under permissive licensing, making them invaluable tools for analyzing broadband coverage and funding opportunities. Licensing information can be found here and here, respectively.1
What are these two datasets?
On March 23, 2020, the Broadband Deployment Accuracy and Technological Availability Act or Broadband DATA Act was enacted2. This led to the FCC’s creation of the National Broadband Map (NBM) in November 20223 and the Broadband Funding Map in May 20234 (documented in July 20235) as the primary methods of publicly releasing these data sets.
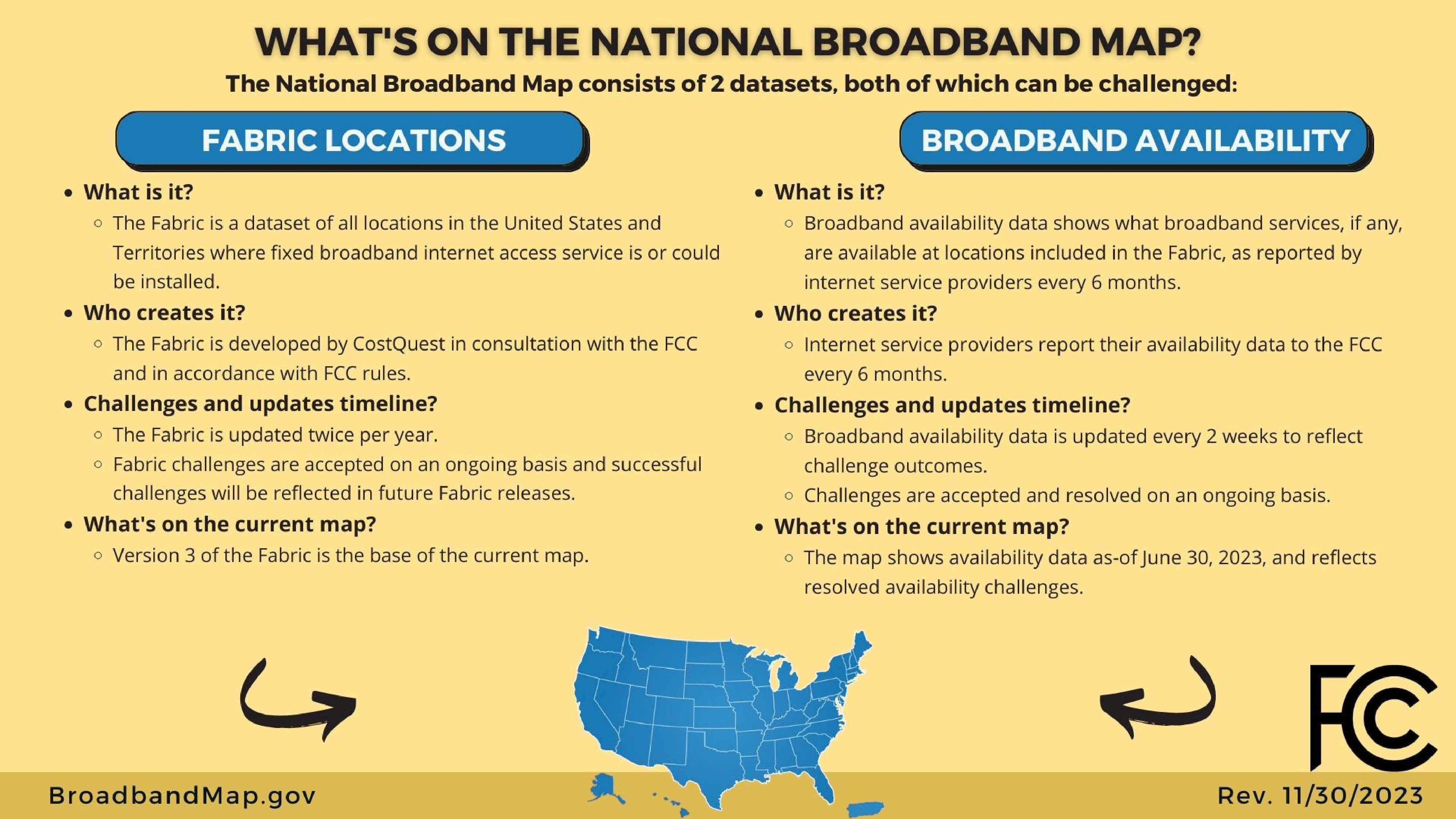
National Broadband Map (NBM)
The NBM offers detailed broadband availability information:
- Identifies providers and technologies at each location.
- Classifies locations as residential, business, or both.
- Localizes data to census blocks or H3 hexagons.
This dataset is an abstraction of the “Fabric” locations data developed by CostQuest. The Fabric provides precise geolocation data for Broadband Serviceable Locations (BSLs), which are updated biannually (June and December) with interim updates every two weeks. The exact coordinates for each locations are only inclued in the Fabric dataset, so using the National Broadband Map data we can only link a record for a location to a Census Block (2020 vintage) or H3 hexagon.
Every location is characterized by:
- Who is providing those services (
frn,provider_id, andbrand_name) - A description of each of the services (
technology,max_advertised_download_speed,max_advertised_upload_speed,low_latency) - Whether the location is characterised as residential, business or both
- Ways to geographically locate it (
state_abbr,block_geoid,h3_res8_id)
A location (see What is a BSL?) can be covered by multiple Internet Services Provides (ISP) with potentially different services and technologies. Hence, it can represented in the data can by many “rows”.
Sometimes the process of collecting those two datasets is called Broadband Data Collection (BDC)
Broadband Funding Map (BFM)
The BFM provides information about “broadband infrastructure deployment projects funded by the Federal government throughout the United States”. The public data:
- Categorizes projects by program and geographic boundaries.
- Highlights funding from four federal agencies across 12 programs, including 1,853 projects as of May 2024.
- Provides a critical resource for identifying areas targeted for infrastructure investment.
The information is structured either at the scale of a specific project inside a program or for the whole program. Hence we have characteristics for each project, including their associated boundaries (territories covered) (see https://ruralinnovation.github.io/proj-fcc-report/fcc_funding.html).
What is a Broadband Serviceable Location (BSL)?
A Broadband Serviceable Location (BSL) is defined as a location in the U.S. where fixed broadband internet access service is available or can be installed. These include:
- Residential BSLs: Housing units or group quarters as defined by the U.S. Census Bureau.
- Business BSLs: Non-residential structures, such as government or nonprofit facilities, on properties without residential locations.
A broadband serviceable location is defined as “a business or residential location in the United States at which fixed broadband Internet access service is, or can be, installed.” A residential BSL includes all residential structures, including structures that are (or contain) housing units or group quarters (as those terms are defined by the United States Census Bureau). A business BSL includes “all non-residential (business, government, non-profit, etc.) structures that are on property without residential locations and that would expect to demand Internet access service.” (source FCC6)
When is this data updated?
NBM has two big releases per year (June and December) and have “unofficial” versions every two weeks to take into account challenges7. Experience has told us that sometimes their release can be faster (more than one per week) or slower. The FCC did not (April 2024) provides a changelog between releases or versions (but the documentation has some of the major changes8).
BFM seems to follow a schedule of update every two weeks but we have not find any specifications.
What is the geographic coverage of these datasets?
- Broadband Availability Data: Covers all U.S. states, Puerto Rico, and U.S. territories.
- Funding Map Data: Varies by program, with coverage reflecting specific project boundaries.
What is “Unserved” vs. “Underserved”?
Served, Unserved and Underseved are overlapping categories at the location level. They can be extended at the “area level”.
If all available internet services at a location have advertised (reported) maximum speeds that are below 25 Mbps downstream speed or below 3 Mbps upstream (25/3 to simplify), then that location is categorized as unserved. If a location has at least one service with maximum speeds that are equal to or above 25/3, but no service with maximum speeds that are equal to or above 100/20, it is categorized as underserved. If a location has at least one service with maximum speeds that are equal to or above 100/20, then that location is categorized as served.
Those definitions are recommended in the FCC’s Broadband Speed Benchmark and can be adapted by every States9.
Quick facts, May 2024:
Broadband Availibility:
Number of BSL: 115 342 225
Number of unique
FRN: 2879
Funding Map:
4 agencies are contributing
The Funding Map consist of 12 programs (1853 projects) with two specific to Puerto Rico (PR) and US territories.
Those projects are classified by FCC in 3 categories: “Area”, “List of locations” and “Middle mile”10
Footnotes
License and Attribution language from the FCC:
Broadband availability data from the BDC, and data from the U.S. Census Bureau that are presented on this site, are offered free and not subject to copyright restriction. Data and content created by government employees within the scope of their employment are not subject to domestic copyright protection under 17 U.S.C. § 105. See, e.g., U.S. Government Works.
While not required, when using in your own work content, data, documentation, code, and related materials from fcc.gov or broadbandmap.fcc.gov, we ask that you provide proper attribution of the data. Examples include:
Source data: FCC Broadband Funding Map
Map layer based on FCC BFM
CostQuest Associates, Inc. and its third-party licensors, as applicable, own all right, title, and interest, including all intellectual property rights, in and to the data for locations reflected in the Fabric (including the Location ID, latitude and longitude, address, unit count, and building type code for each location in the Fabric). CostQuest is granted certain rights to Fabric correction submissions for the purpose of correcting or otherwise modifying BDC Fabric data. Broadband service providers, governmental entities, and other third parties are able to license Fabric data, including any changes to Fabric data that have been made as a result of challenges, at no cost for purposes of their participation in the FCC’s Broadband Data Collection.↩︎Broadband_Data_and_Mapping_Background_and_Issues_for_the_117th_Congress↩︎
https://www.fcc.gov/news-events/notes/2022/11/18/new-broadband-maps-are-finally-here↩︎
https://www.fcc.gov/sites/default/files/bdc-challenge-overview.pdf↩︎
See “Change Log” https://us-fcc.app.box.com/v/bdc-data-downloads-output↩︎
Page 4 https://www.pewtrusts.org/-/media/assets/2023/06/un–and-underserved-definitions-ta-memo-pdf.pdf↩︎
In May 2024 no “Middle mile” were present↩︎